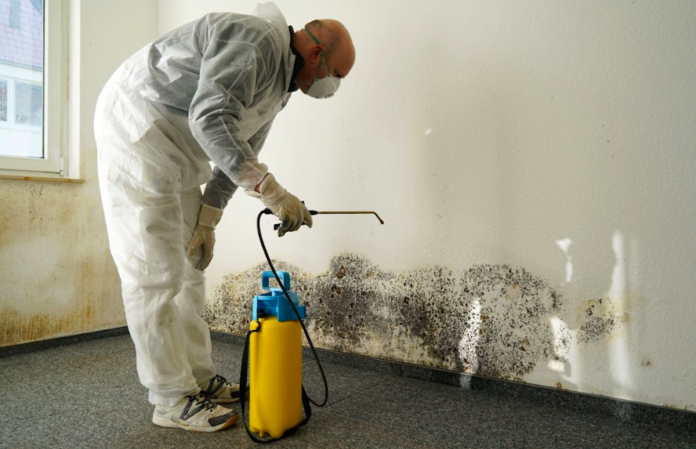
Mold can be a significant problem for homeowners. Excessive moisture in your home can foster the growth of mold. Unfortunately, moisture can come from many sources within your home. Common sources include leaks in pipes or undetected holes in the roof. Adverse weather that leads to flooding can also put your home at risk for mold if you don’t promptly eliminate the residual moisture.
Understanding Mold
Mold is a member of the fungi family, with various types capable of thriving both outdoors and indoors. Outdoors, mold serves an important role by aiding in the decomposition of organic material. However, when mold grows indoors, it can cause problems for both your home’s structure and the health of its occupants. If you discover mold in your home, it’s advisable to hire a professional service such as Mold Zero Services LLC or other providers to ensure a head start.
Mold spreads through spores and flourishes in moist, warm conditions. If these spores land on damp areas or materials, they begin to grow. Unfortunately, mold can grow on almost any surface, including paper, fabric, and wood, gradually consuming the material on which it grows.
Spores can enter your home through the air, via open windows or doors. They can also attach to objects, people, or pets. Additionally, certain activities, like taking hot showers, drying clothes indoors, cooking with uncovered pots, or using humidifiers, can all increase indoor moisture and promote mold growth.
Potential Health Effects Of Mold Exposure
The presence of indoor mold is a cause for concern, especially following recent flooding or significant leaks. Unfortunately, mold poses health risks, particularly for family members with allergies, asthma, respiratory issues, or weakened immune systems. Here are some health issues that can arise from exposure to mold at home:
- Breathing Problems
Indoor mold releases spores into the air, which can be harmful to individuals with sensitivities. Continuous exposure can irritate the lungs, nose, and throat, and it is particularly harmful to those with pre-existing respiratory issues, asthma, or chronic lung conditions.
- Allergic Reactions
People sensitive or allergic to mold may exhibit symptoms upon exposure. Similar to other allergies, mold exposure can affect the upper respiratory tract, triggering symptoms such as:
- Itchy nose
- Runny or congested nose
- Throat irritation
- Sneezing
- Watery eyes
It’s crucial to prevent mold growth in the first place. If a family member starts to exhibit these symptoms, it may indicate the presence of mold.
- Asthma
For individuals with asthma, exposure to mold spores can trigger an attack. Prompt use of an inhaler is crucial to manage symptoms, which may include wheezing, shortness of breath, and coughing. In most cases, symptoms will only subside with proper treatment and thorough cleaning to eliminate the mold in your home.
- Aspergillosis
The Aspergillus mold can cause aspergillosis in certain individuals. Aspergillus is a common type of fungus found both indoors and outdoors. Although most people are exposed to this mold daily without adverse effects, some may develop aspergillosis. Those with weakened immune systems or existing lung conditions are especially vulnerable to severe reactions upon exposure to these spores.
Symptoms of aspergillosis can vary depending on the affected organs, but they often include fever and chills, shortness of breath, headache, chest pain, and coughing up blood.
Ways To Prevent Mold In Your Home
Mold is almost ubiquitous and requires moisture to grow. To reduce the likelihood of indoor mold growth and Residential Mold Remediation, consider the following measures:
- Keep the indoor environment properly ventilated. Make sure your home has good ventilation at all times. A straightforward approach is to open the windows if the weather allows. You can switch on the exhaust fans, especially during showering, bathing, cooking, washing, and drying clothes.
- Maintain low indoor humidity. Limit the use of humidifiers and keep indoor plants to a minimum.
- Control indoor moisture and dampness. Regular inspections can help identify potential sources of leaks. Promptly repair any plumbing issues, particularly damaged water pipes, blocked gutters, or leaking roofs. If water does enter your home, clean and thoroughly dry all affected carpets and other building materials. Dispose of any materials that cannot be properly cleaned and dried.
As evidenced, mold growth in your home can be prevented. Regular cleaning and maintenance of potential problem areas can help keep your home mold-free.
Final Thoughts
Mold is present almost everywhere, making its complete eradication impossible. While the presence of mold does not always result in health problems, its prompt removal is essential. If you discover mold, eliminate it immediately. Timely removal will help prevent respiratory issues and ensure the safety of your indoor environment.